Peter Certo / the Washington Spectator & Lou Dubose / The Washington Spectator – 2015-05-21 00:35:04
http://washingtonspectator.org/accounting-for-the-pentagon/
Accounting for the Pentagon
The debate over defense spending isn’t what it looks like
Peter Certo / the Washington Spectator
(May 1, 2015) — A battle is raging over how much money Americans will sink into the Pentagon next year. At least, that’s what it looks like.
The Republican Party’s deficit hawks have clashed with its defense hawks over another hike in military spending. President Barack Obama, meanwhile, has vowed to veto any spending bill that underfunds his domestic priorities, which already have to compete with a military budget that gobbles up over half of federal discretionary spending.
There are differences at play in the spending priorities between — and within — the two major parties. But when it comes to Pentagon spending, the White House and Congressional Republicans aren’t really squabbling about hard numbers. They’re just arguing about which account to write them in.
By some estimates, total US military spending tops $1 trillion each year, but by far the largest share — about half or more — goes the Pentagon’s so-called “base budget,” which is supposed to cover salaries, administration, weapons acquisitions, research and development. Billions more go to the Overseas Contingency Operations fund, or OCO, to cover “emergency” wartime expenses that can’t be predictably budgeted over the long term.
Those two accounts make up the bulk of conventional military spending, which Obama and most Congressional Republicans want to increase. So what are they arguing about? In its latest budget blueprint, the White House requested the largest base budget in history — $534 billion — plus $51 billion for war spending on the OCO account.
This proposal has a legal problem. That base budget, which comes it at $38 billion over last year’s, calls for several billion dollars more than what’s allowed under “sequestration” spending caps passed by Congress in 2011. Unless lawmakers oblige the administration’s request to lift those caps — which is unlikely, since they also cover domestic spending opposed by Republicans — Obama’s base budget would be subject to automatic cuts.
How did Republicans in Congress respond?
Both the House and the Senate passed resolutions putting the base budget at the maximum allowable $523 billion. Then they pumped tens of billions extra into the OCO account — which, as “emergency” spending, is supposedly not constrained by the caps — bringing it to $96 billion.
The Senate version marked $89 billion of that — that is, $38 billion above Obama’s OCO request — specifically for the Pentagon. Not coincidentally, that’s exactly the amount that Obama wants to increase the base budget by, except it goes into a separate account that’s not subject to spending caps.
The GOP plan “keeps the budget caps on ‘regular’ military spending to satisfy the deficit hawks, while breaking them, with huge amounts stuffed into the war budget, to satisfy the defense hawks,” explains Miriam Pemberton, a research fellow (and my colleague) at the Institute for Policy Studies.
With the Afghan war slowly winding down and the ISIS war running a relatively modest tab (fiscally, anyway), that extra OCO money has nothing to do with any wars the US is fighting. “More likely,” writes military-spending expert William Hartung, “the bulk of the funds will be wielded simply to take pressure off the Pentagon’s base budget so it can continue to pay for staggeringly expensive projects like the F-35 combat aircraft and a new generation of ballistic missile submarines.”
Secretary of Defense Ashton Carter has objected to this particular accounting trick, complaining — along with some military leaders — that using year-to-year OCO budgeting makes it more difficult for the military to make long-term investments.
There’s also no guarantee that Obama, who seems to object more to spending caps than to misallocating military funds, would sign off on such a measure.
But other officials have voiced support for harvesting the extra funds by any means necessary. Using the slush fund is “a far better outcome than sequestration. There’s no argument about that,” Army Secretary Jack McHugh told Congress in March. “I don’t know how to fix this,” added his Air Force counterpart Deborah Lee James, “but if the use of OCO, if it’s allowable, or if you can find a way to make it allowable . . . I’m all in favor.”
Neither the White House blueprint nor the GOP’s has much chance of becoming law on its own. But with spending caps unlikely to go away anytime soon, the OCO slush fund is likely to remain an appealing option for enthusiasts of military spending — even while new funds for health care, jobs, education, environmental protection, and other domestic priorities remain locked beneath the caps.
“I fear there is high risk it becomes permanent,” said former White House budget official Gordon Adams. It’s simply “too tempting” for the Pentagon, GOP appropriators, “and even the White House.”
Peter Certo is the editor of Foreign Policy In Focus and the deputy editor of OtherWords, projects of the Institute for Policy Studies.
A Farewell to Arms?
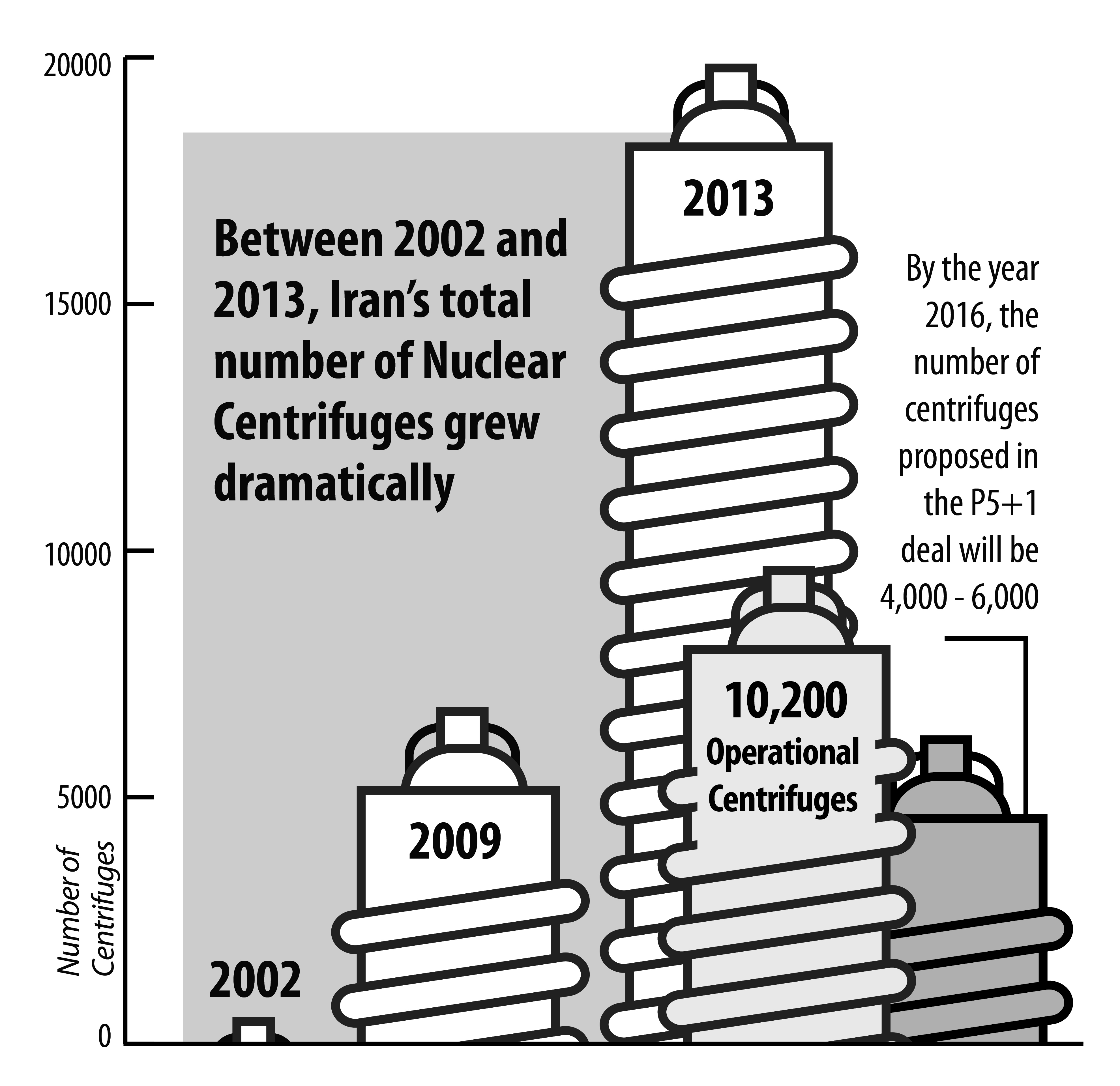
In 2002, Iran had 200 centrifuges to enrich uranium.
By 2009, it had 7,000. By 2013, 20,000
Lou Dubose / The Washington Spectator
(May 1, 2015) — In 2002, as US military forces mobilized to invade Iraq, Iran possessed 200 centrifuges to enrich uranium. By 2009, that number had grown to 7,000. By 2013, Iran had acquired 20,000, with more than 10,000 enriching uranium. The acquisition of centrifuges, and the bringing of existing centrifuges online, was stopped by the P5+1 negotiations that began in 2013.
Those numbers are available and verifiable, because Iran, along with 188 nations, is a signatory to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, and has opened its facilities to inspection by the International Atomic Energy Agency. North Korea was a signatory to the treaty but withdrew. Pakistan, India, and most notably Israel are not signatories. All three non-signatory nations have nuclear warheads and delivery systems.
Israel has modified US F-15 and F-16 fighter jets to carry nuclear bombs. It has land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles. Israel also has, according to a 2012 report in Der Spiegel, three German-built Dolphin Class submarines armed with Popeye Turbo sea-launched cruise missiles that can deliver 200 kg nuclear warheads. From the Persian Gulf, the sub-launched missiles with a range of 1,000 miles can strike targets inside Iran.
All of the P5 (permanent members of UN Security Council — China, France, Russia, the UK, and the US) have substantial nuclear arsenals. Germany, the nation designated as Plus 1, imports nuclear weapons from the US and produces warheads for France. Germany remains classified as a non-nuclear state.
The initial phase of the P5+1 negotiations ended on April 2, with an agreement to limit Iran’s nuclear-weapons capability. The deadline for a detailed finalized agreement is June 2015.