/arc-anglerfish-arc2-prod-mco.s3.amazonaws.com/public/ED3XTEYCGRDAFJUS7ZFFITQW2A.jpg)
South Korea Disputes US Troop Cost
Josh Smith / Reuters & The Herald Sun (Australia)
(December 18, 2019) — South Korea and the United States have failed to reach an agreement over Seoul’s contribution towards hosting some 28,500 US troops, ending two days of talks that were the last before their existing deal expires on December 31.
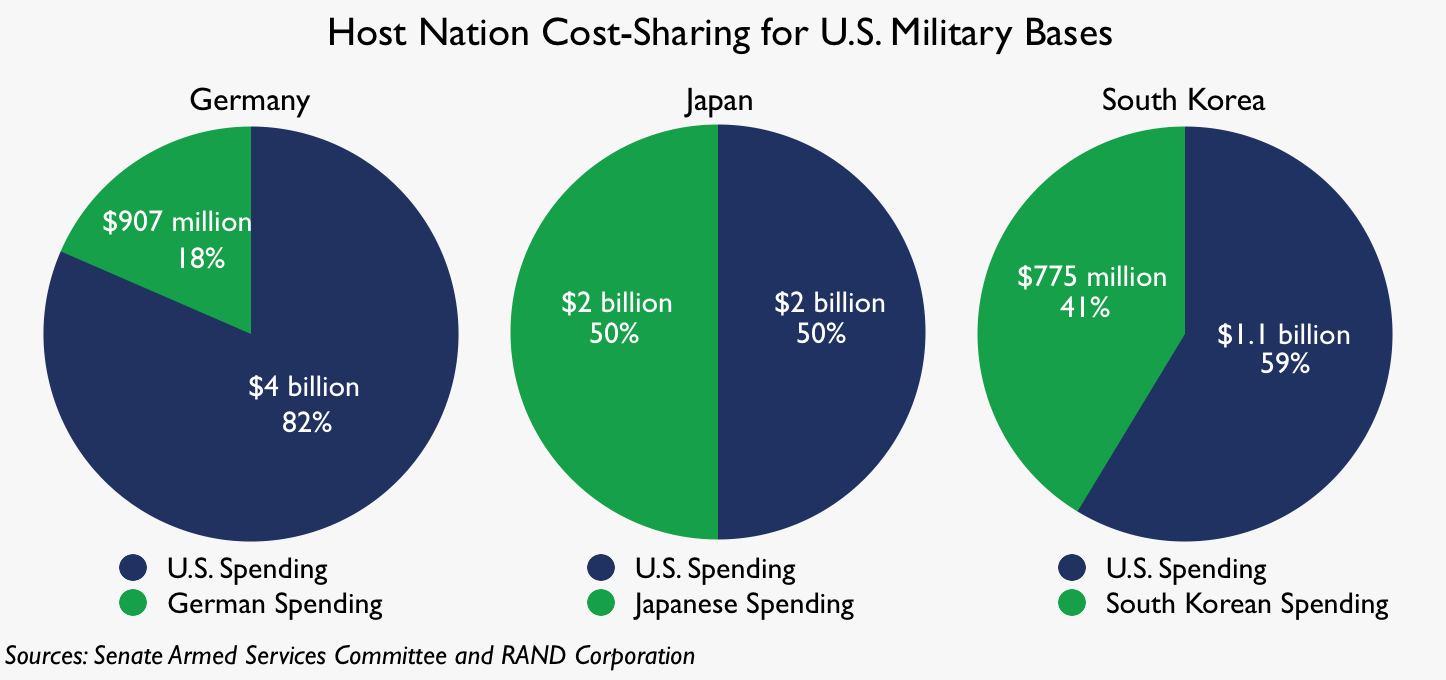
South Korean lawmakers have said Washington is seeking up to $US5 billion ($7.3 billion) a year, more than five times the amount Seoul agreed to pay this year.
As part of his ‘America First” policy, US President Donald Trump has demanded that many US allies, including NATO members and Japan, pay more towards defence.
He has frequently accused South Korea of being a rich nation that is profiting off the US military forces, which are stationed in the country as a legacy of the 1950-1953 Korean War and continued threats from North Korea.
The lack of a deal in talks led by South Korea’s chief negotiator Jeong Eun-bo and his US counterpart, James DeHart, could result in a repeat of last year when the two countries missed a year-end deadline but reached a retroactive agreement in the new year.
Some experts, both US and Korean, have warned that if no agreement is reached, it could throw the entire future of the US presence in South Korea into doubt.
The next set of talks will be in the United States in January, with the exact timing still to be determined.
South Korea’s Foreign Ministry said their negotiators emphasised the need for “fair, reasonable and mutually acceptable agreements,” that will strengthen the alliance.
“The two sides have expanded their understanding of each other through many discussions despite differences in their positions on various issues, and decided to continue close consultations,” it said in a statement.
A spokesman for the US Embassy in Seoul declined to comment.
The dispute has been a rare public sign of discord in the “airtight” alliance that has for 70 years formed a buffer against North Korean aggression. The two Koreas remain in a technical state of war under a truce, not a peace treaty, that ended the Korean War.
There have been several public protests in South Korea against the US calls for more money.
South Koreans overwhelmingly oppose paying more, a survey released on Monday by the Chicago Council of Global Affairs found, with only 4 per cent of respondents saying Seoul should meet Trump’s demands.
Still, 74 per cent of those questioned said they support the long-term stationing of American troops in South Korea.
If no deal is reached, the most immediate effect may be on thousands of South Korean civilians who work for the US military and who could be placed on unpaid leave.
South Korea Rejects US Troop Cost Demands, Talks End Without Deal
No more talks scheduled before deal expires
(December 18, 2019) — Two days of negotiations between the US and South Korea on cost-sharing of the US military presence have ended in failure, and there are no more talks scheduled before the existing deal expires on December 31.
President Trump’s last minute demands for a massive increase could be shaping up to be a huge mistake, as South Korea was already paying more than most nations do for US troops, and had agreed to a more modest increase. Getting from $800 million per year to around $1 billion per year was one thing, but Trump’s zero-hero demand for $5 billion per year angered many in South Korea.
The US didn’t do a good job of justifying this unprecedented increase, either, with administration officials arguing that South Korea is rich and therefore could afford it. With South Korea working on improved military ties with China and making peace overtures to North Korea, however, it isn’t clear that what they could afford is even necessary.
South Korea says that work will continue on a fair and reasonable agreement, while US officials have refused all comment. This once again gives the impression that the US is intractable on the matter, which is driving a lot of popular opposition in South Korea.
Posted in accordance with Title 17, Section 107, US Code, for noncommercial, educational purposes.